The Reproductive System
Video Project Puberty
Brain Pop Video
Learn More Here

The Female Reproductive System
The Menstrual Cycle The endocrine system controls egg maturation and release andthickening of the lining of the uterus in a process called the menstrual (MEN stroo ul) cycle.The menstrual cycle takes about 28 days and has three parts.
During the first part of the cycle, eggs grow and mature in the ovaries, while the broken down lining of the uterus leaves the body. In the second part of the cycle, mature eggs are released from the ovaries and the lining of the uterus thickens. In the third part of the cycle,unfertilized eggs and the thickened lining break down. The lining leaves the body in the first part of the next cycle.
Adolescence Through Adulthood
Video Project Puberty
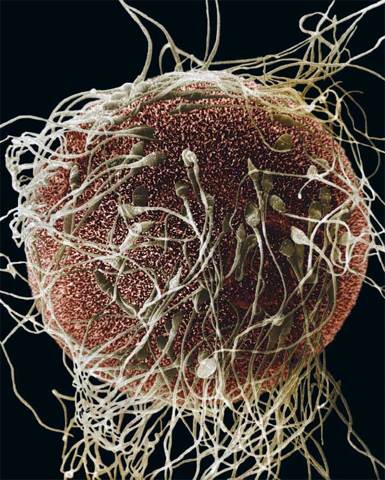
Strands of Hair?
The things that look like strands of hair are sperm, the male reproductive cells. The red structure is an egg, the female reproductive cell. Why are there so many sperm but only one egg?
Brain Pop Video
Learn More Here
We have read how the endocrine system works with other organ systems and helps the body grow and maintain homeostasis.The endocrine system has another very important function—to ensure that humans can reproduce. Some of the organs of the endocrine system produce hormones that help humans reproduce.
Reproduction is the process by which new organisms are produced. Reproduction ises
ntial to the continuation of life on Earth.
A male and a female each have special organs for reproduction. Organs in the male repoductive system are different from those in the female reproductive system.
Human reproductive cells, called gametes (GA meets), are made by the male and female reproductive systems. Male gametes are called sperm. Female gametes are called ova (OH vah; singular ovum), or eggs.
As shown in the photo at the beginning of the lesson, a sperm joins with an egg in a reproductive process called fertilization. The cell that forms when a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell is called a zygote (ZI goht).
A zygote is the first cell of a new human. It contains genetic information from both the sperm and the ovum. The zygote will grow and develop in the female’s reproductive system.
1.  Reading Check How do gametes enable humans to reproduce?
Reading Check How do gametes enable humans to reproduce?
 Reading Check How do gametes enable humans to reproduce?
Reading Check How do gametes enable humans to reproduce?
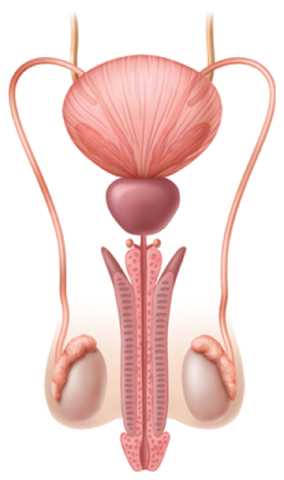
The Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system, shown in Figure 1, produces sperm and delivers it to the female reproductive system. Sperm are produced in the testes (TES teez; singular, testis).Sperm develop inside each testis and then are stored in tubes called sperm ducts. Sperm matures in the sperm ducts.
The testes also produce a hormone called testosterone. Testosterone helps sperm change from round cells to long, slender cells that can swim. Once sperm have fully developed,they can travel to the penis. The penis is a tube like structure that delivers sperm to the female reproductive system. Sperm are transported in a fluid called semen (SEE mun).Semen contains millions of sperm and nutrients that provide the sperm with energy.
2. Key Concept Check What does the male reproductive system do?

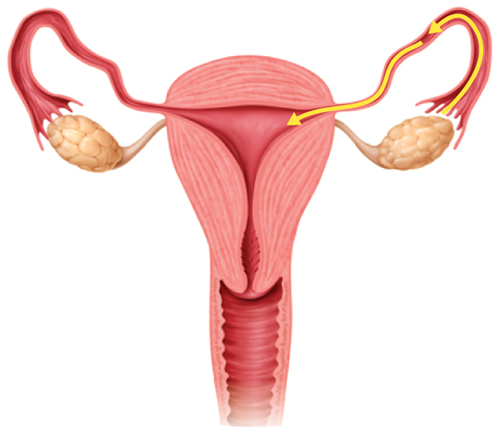
Figure 1 Males and females have specialized organs for reproduction.
The Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system contains two ovaries, as shown in Figure 1. Eggs growand mature in the ovaries. Two hormones made by the ovaries, estrogen (ES truh jun)and progesterone (proh JES tuh rohn), help eggs mature. Once mature, eggs arereleased from the ovaries and enter the fallopian tubes. As shown in Figure 1, thefallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus.
If sperm are also present in the fallopian tube, fertilization can occur as the egg
enters the fallopian tube. Sperm enter the female reproductive system through the vagina,a tube-shaped organ that leads to the uterus. A fertilized egg, or zygote, can move through the fallopian tube and attach inside the uterus.
enters the fallopian tube. Sperm enter the female reproductive system through the vagina,a tube-shaped organ that leads to the uterus. A fertilized egg, or zygote, can move through the fallopian tube and attach inside the uterus.
If there are no sperm in the fallopian tube, the egg will not be fertilized. However, it will still travel through the fallopian tube and uterus and then break down.
The Menstrual Cycle The endocrine system controls egg maturation and release andthickening of the lining of the uterus in a process called the menstrual (MEN stroo ul) cycle.The menstrual cycle takes about 28 days and has three parts.
During the first part of the cycle, eggs grow and mature in the ovaries, while the broken down lining of the uterus leaves the body. In the second part of the cycle, mature eggs are released from the ovaries and the lining of the uterus thickens. In the third part of the cycle,unfertilized eggs and the thickened lining break down. The lining leaves the body in the first part of the next cycle.
3. Key Concept Check What does the female reproductive system do?
WORD ORIGIN
zygote
from Greek zygoun, means “to join”
from Greek zygoun, means “to join”
4
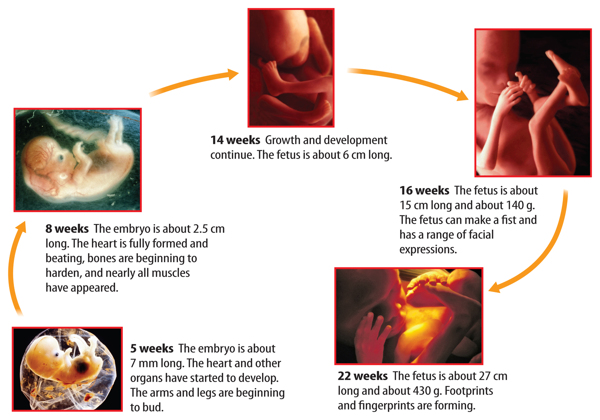
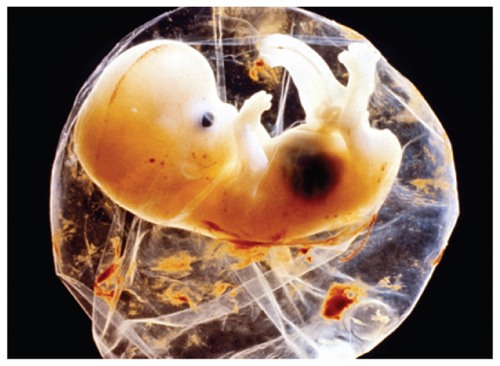
As shown in Figure 2, humans develop in many stages. You have read that when asperm fertilizes an egg, a zygote forms. The zygote develops into an embryo (EMbree oh). An embryo is a ball-shaped structure that attaches inside the uterus andcontinues to grow.
The embryo develops into a fetus, the last stage before birth. It takes about 38 weeksfor a fertilized egg to fully develop. This developmental period is called pregnancy.During this period, the organ systems of the fetus will develop and the fetus will getlarger. Pregnancy ends with birth. During birth, the endocrine system releaseshormones that help the uterus push the fetus through the vagina and out of the body.
From Birth Through Childhood
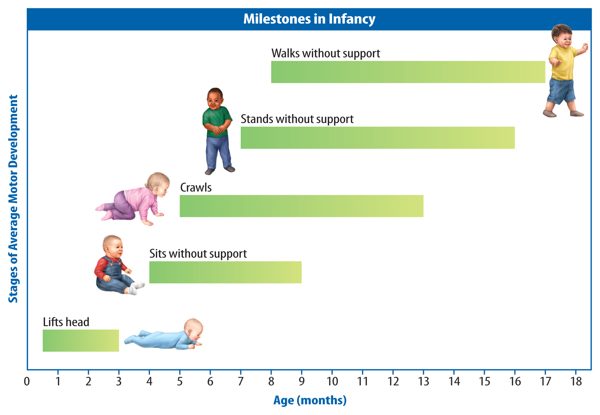
The first life stage after birth is infancy, the first 2 years of life. During infancy, themuscular and nervous systems develop and an infant begins walking, as shown inFigure 3. Growth and development continue in childhood, which is from about 2 yearsto about 12 years of age. Bones in the skeletal system grow longer and stronger, andthe lymphatic system matures.
Adolescence Through Adulthood
Adolescence follows childhood. During adolescence, growth of the skeletal andmuscular systems continues. Organs such as the lungs and kidneys get larger. As theendocrine system develops, the male and female reproductive systems mature. Theperiod of time during which the reproductive system matures is called puberty
Interactive Information on Puberty
Interactive Information on Puberty
After adolescence is adulthood, as shown in Figure 4. During adulthood, humanscontinue to change. In later adulthood, hair turns gray, wrinkles might form in the skin,and bones become weaker in a process called aging. Aging is a slow process that canlast for decades.
1. Key Concept Check How do humans change during adulthood?
Lesson Review - Visual Summary
Sperm are produced and develop in the testes.
Eggs grow and mature in the ovaries.
During pregnancy, a zygote develops into an embryo and then into a fetus.
What do you think NOW?
You first read the statements below at the beginning of the lesson.
1. The testes produce sperm.
2. Puberty occurs during infancy.
Did you change your mind about whether you agree or disagree with the statements?Rewrite any false statements to make them true.
Use Vocabulary
1. Sperm and ova are types of __________.
2. Distinguish between an ovum and a zygote.
3. Define fertilization in your own words.
Understand Key Concepts
4. The period between birth and 2 years is called
A.adolescence.
B.adulthood.
C.childhood.
D.infancy.
5. Compare the functions of the ovaries and the testes.
6. Distinguish between a zygote and a fetus.
7. Which hormone helps the cells produced in the system below mature?
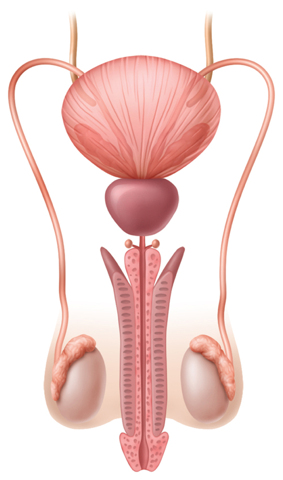

A.estrogen
B.insulin
C.progesterone
D.testosterone
8. Which connects the ovaries to the uterus?
A.bladder
B.cervix
C.fallopian tubes
D.seminiferous tubules
9. Which system works with the reproductive system?
A.endocrine
B.excretory
C.respiratory
D.skeletal
Interpret Graphics
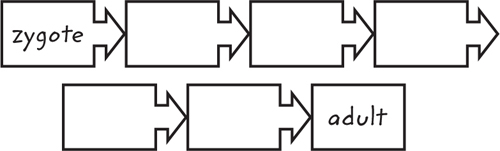
10. Summarize Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to show the stages oflife.

11. Evaluate the changes in aging using the photo below.
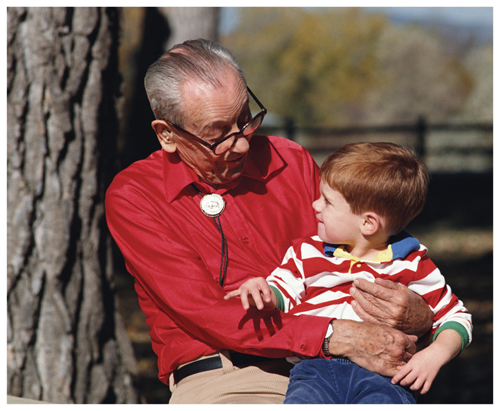


PhotoLink/Getty Images
Critical Thinking
12. Hypothesize why development before birth takes a long time, about 38 weeks.
13. Summarize the role of puberty in the transition from adolescence to adulthood.
14. Compare the functions of the male and female reproductive systems.
15. Describe how the endocrine system and the reproductive system are related.
16. Why so many sperm and only one egg? To ensure that the one sperm is able to reach an egg, in
order to fertilise it.
16. Why so many sperm and only one egg? To ensure that the one sperm is able to reach an egg, in
order to fertilise it.



No comments:
Post a Comment