Lymphatic, Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
Visit Mrs. Sandovals New Website!
Links Games Virus and the Human Body Game Virus Game
Click here to see Cellular respiration power-point.
Click here to view the Respiration PowerPoint.
Click here to see the heart in action!
Click here to see the circulatory system in action
Click here to label the parts of the heart!
Click here to label the parts of the respiratory system
Amazing Blood Facts
 Your lymphatic system has three main functions: removing excess fluid around organs, producing white blood cells, and absorbing and transporting fats. The lymphatic system helps your body maintain fluid homeostasis. About 65 percent of the human body is water. Most of this water is inside cells. Sometimes, when water, wastes, and nutrients move between capillaries and organs, not all of the fluid is taken up by the organs. When fluid builds up around organs, swelling can occur. To prevent swelling, the lymphatic system removes the fluid.
Your lymphatic system has three main functions: removing excess fluid around organs, producing white blood cells, and absorbing and transporting fats. The lymphatic system helps your body maintain fluid homeostasis. About 65 percent of the human body is water. Most of this water is inside cells. Sometimes, when water, wastes, and nutrients move between capillaries and organs, not all of the fluid is taken up by the organs. When fluid builds up around organs, swelling can occur. To prevent swelling, the lymphatic system removes the fluid.
 Visual Check How long did it take for the lymphocyte to completely surround the bacterium?
Visual Check How long did it take for the lymphocyte to completely surround the bacterium?
The Circulatory System
 Visual Check To which blood group can type A donate?
Visual Check To which blood group can type A donate?
You have read about how the body converts food into nutrients and how the small intestine absorbs nutrients. But how do the oxygen you breathe in and the nutrients absorbed by the small intestine get to the rest of the body?
And how do waste products leave the body?
Click here to see Cellular respiration power-point.
Click here to view the Respiration PowerPoint.
Click here to see the heart in action!
Click here to see the circulatory system in action
Click here to label the parts of the heart!
Click here to label the parts of the respiratory system
Amazing Blood Facts
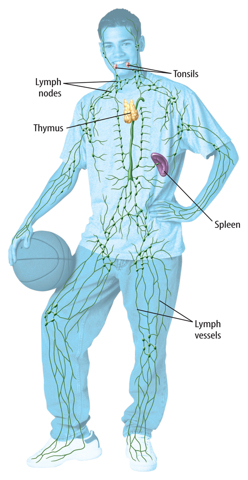
The Lymphatic System
Have you ever had a cold and found it painful to swallow? This can happen if your tonsils swell. Tonsils are small organs on both sides of your throat. They are part of the lymphatic (lihm FA tihk) system.
The spleen, the thymus, bone marrow, and lymph nodes also are parts of the lymphatic system. The spleen stores blood for use in an emergency. The thymus, the spleen, and bone marrow make white blood cells.
 Your lymphatic system has three main functions: removing excess fluid around organs, producing white blood cells, and absorbing and transporting fats. The lymphatic system helps your body maintain fluid homeostasis. About 65 percent of the human body is water. Most of this water is inside cells. Sometimes, when water, wastes, and nutrients move between capillaries and organs, not all of the fluid is taken up by the organs. When fluid builds up around organs, swelling can occur. To prevent swelling, the lymphatic system removes the fluid.
Your lymphatic system has three main functions: removing excess fluid around organs, producing white blood cells, and absorbing and transporting fats. The lymphatic system helps your body maintain fluid homeostasis. About 65 percent of the human body is water. Most of this water is inside cells. Sometimes, when water, wastes, and nutrients move between capillaries and organs, not all of the fluid is taken up by the organs. When fluid builds up around organs, swelling can occur. To prevent swelling, the lymphatic system removes the fluid.
4.  Reading Check Identify a function of the lymphatic system.
Reading Check Identify a function of the lymphatic system.
 Reading Check Identify a function of the lymphatic system.
Reading Check Identify a function of the lymphatic system.
Lymph vessels are all over your body, as shown in Figure 9. Fluid that travels through the lymph vessels flows into organs called lymph nodes. Humans have more than 500 lymph nodes. The lymph nodes work together and protect the body by removing toxins, wastes, and other harmful substances.
The lymphatic system makes white blood cells. They help the body defend against infection. There are many different types of white blood cells. Alymphocyte (LIHM fuh sites) is a type of white blood cell that is made in the thymus, the spleen, or the bone marrow. Lymphocytes protect the body by traveling through the circulatory system, defending against infection.
C Squared Studios/Getty Images
Figure 9 Lymph vessels are throughout your body.
Immunity
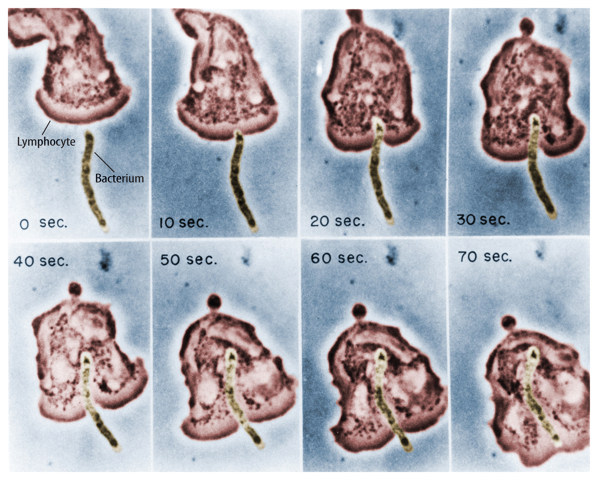
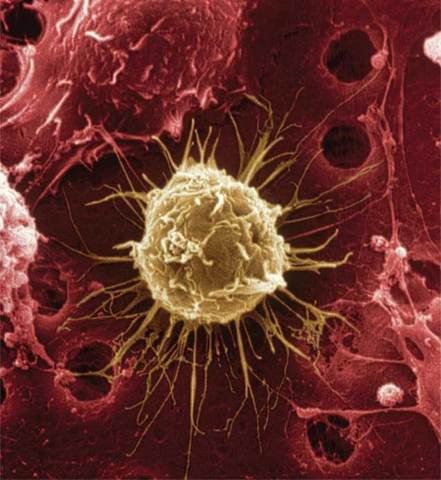
The lymphatic system protects your body from harmful substances and infection. The resistance to specific pathogens, or disease-causing agents, is called immunity. The skeletal system produces immune cells, and the circulatory system transports them throughout the body. Immune cells include lymphocytes and other white blood cells. These cells detect viruses, bacteria,and other foreign substances that are not normally made in the body. The immune cells attack and destroy them, as shown in Figure 10.
If the body is exposed to the same bacteria, virus, or substance later, some immune cells remember and make proteins called antibodies. These antibodies recognize specific proteins on the harmful agent and help the body fight infection faster. Because there are many different types of bacteria and viruses,humans make billions of different types of antibodies. Each type of antibody responds to a different harmful agent.

Omikron/Photo Researchers
Figure 10 Lymphocytes surround bacteria and destroy or remove them from the body.
 Visual Check How long did it take for the lymphocyte to completely surround the bacterium?
Visual Check How long did it take for the lymphocyte to completely surround the bacterium?
Types of Diseases
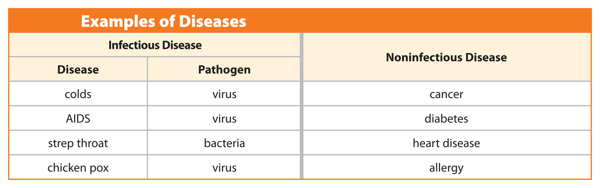
There are two main groups of diseases—infectious and noninfectious—as shown in Table2. Infectious diseases are caused by pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses. Infectious diseases are usually contagious, which means they can be spread from one person to another. The flu is an example of an infectious disease. Viruses that invade organ systems of the body, such as the respiratory system, cause infectious diseases.
A noninfectious disease is caused by the environment or a genetic disorder, not a pathogen. Skin cancer, diabetes, and allergies are examples of noninfectious diseases. Noninfectious diseases are not contagious and cannot be spread from one person to another.

Table 2 Diseases are classified into two main groups based on whether they are caused by pathogens.
Lines of Defense
The human body has many ways of protecting itself from viruses, bacteria, and harmful substances. Skin and mucus (MYEW kus) are parts of the first line of defense. They prevent toxins and other substances from entering the body.Mucus is a thick, gel-like substance in the nostrils, trachea, and lungs. Mucus traps harmful substances and prevents them from entering your body.
The second line of defense is the immune response. In the immune response,white blood cells attack and destroy harmful substances, as shown in Figure 10.
The third line of defense protects your body against substances that have infected the body before. As you have read, immune cells make antibodies that destroy the harmful substances. Vaccines are used to help the body develop antibodies against infectious diseases. For example, many people get an influenza vaccine annually to protect them against the flu.
5. Key Concept Check How does the body defend itself from harmful invaders?
The Circulatory System
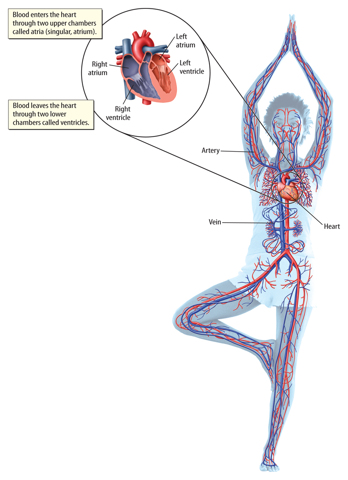
As shown in Figure 8, the heart, blood, and blood vessels make up the circulatory system. It transports nutrients, gases, wastes, and other substances through the body. Blood vessels transport blood to all organs in the body.Because your body uses oxygen and nutrients continually, your circulatory system transports blood between the heart, lungs, and other organs more than 1,000 times each day!
Figure 8 The circulatory system transports nutrients and oxygen to all parts ofthe body and removes wastes, such as CO2.
Heart and Vessels
Your heart is made up of muscle cells that constantly contract and relax.Contractions pump blood in your heart out of the heart to the rest of your body.When your heart muscles relax, blood from the rest of your body enters the heart.
Your heart is made up of muscle cells that constantly contract and relax.Contractions pump blood in your heart out of the heart to the rest of your body.When your heart muscles relax, blood from the rest of your body enters the heart.
Blood travels through your body in tiny tubes called vessels. If all the blood vessels in your body were laid end-to-end in a single line, it would be more than 95,000 km long.
The three main types of blood vessels are arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Arteries carry blood away from your heart. Usually this blood is oxygen-rich andc ontains nutrients, except for the blood in the pulmonary arteries that contains CO2.
Arteries are large and surrounded by muscle cells that help blood move through the vessels faster.
Veins transport blood that contains CO2 back to your heart, except for the blood in the pulmonary veins, which is oxygen-rich.
Capillaries are very tiny vessels that enable oxygen, CO2, and nutrients to move between your circulatory system and your entire body.
You just read that capillaries surround the alveoli in your lungs. Capillaries also surround the small intestine, where they absorb nutrients and transport them to the rest of the body.
3. Key Concept Check How do nutrients travel through the body?
Blood
The blood that circulates through vessels has several parts. The liquid part of blood is called plasma and contains nutrients, water, and CO2. Blood also contains red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen. Platelets help the body heal when you get a cut. White blood cells helpthe body defend itself from toxins and diseases.
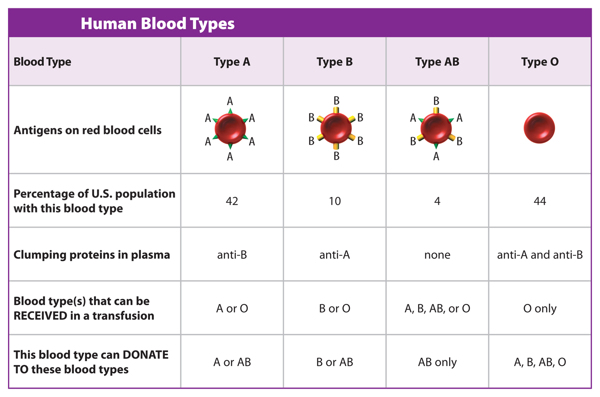
Everyone has red blood cells. However, different people have different proteins on the surfaces of their red blood cells, as shown in Table2.Scientists classify these different red blood cell proteins into groups called blood types.
People with A proteins on their red blood cells have type A blood. People with B proteins on their red blood cells have type B blood. Some people have both A and B proteins on their red blood cells. They have type AB blood. People with type O blood have neither A nor B proteins on the surfaces of their red blood cells.
Medical professionals use blood types to determine which type of blood a person can receive from a blood donor. For example, because people with type O blood have no proteins on the surfaces of their red blood cells, they can receive blood only from a donor who also has type O blood.
Table 1 The red blood cells of each blood type have different proteins on their surfaces.
 Visual Check To which blood group can type A donate?
Visual Check To which blood group can type A donate?
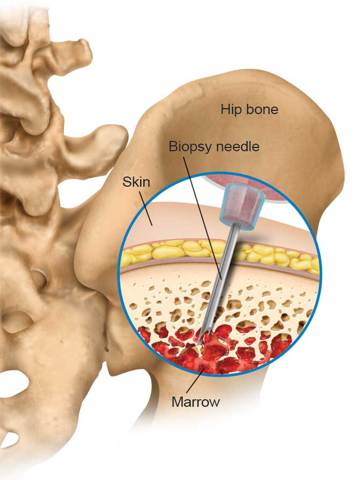
Why might you need new bone marrow?
In healthy bone marrow, a stem cell can develop into different types of blood cells.
Healthy blood cells are essential to overall health. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body. Some white blood cells fight infections. Platelets help stop bleeding. A bone marrow transplant is sometimes necessary when a disease interferes with the body’s ability to produce healthy blood cells.
Bone marrow is a tissue found inside some of the bones in your body. Healthy bone marrow contains cells that can develop into white blood cells, red blood cells, or platelets. Some diseases, such as leukemia and sickle cell disease,affect bone marrow. Replacing malfunctioning bone marrow with healthy bone marrow can help treat these diseases.
A bone marrow transplant involves several steps. The patient receiving the bone marrow must have treatments to destroy his or her unhealthy bone marrow. Healthy bone marrow must be obtained for the transplant. Sometimes,the patient’s own bone marrow can be treated and used for transplant. This transplant has the greatest chance of success. Other transplants involve healthy bone marrow donated by another person. The bone marrow must be tested to ensure that it is a good match for the patient.
The bone marrow donor undergoes a procedure called harvesting. Bone marrow is taken from the donor’s pelvic bone. The donor’s body replaces the harvested bone marrow, so there are no long-term effects for the donor.
The donated bone marrow is introduced into the patient’s bloodstream. If the transplant is successful, the new bone marrow moves into the bone cavities and begins producing healthy blood cells.
And how do waste products leave the body?
The Respiratory System
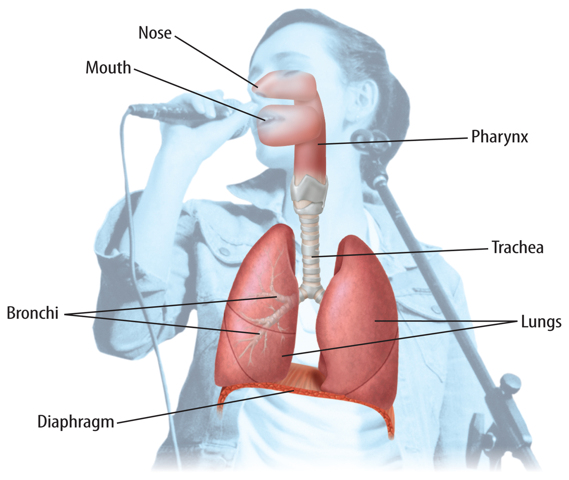
The respiratory system, shown in Figure 6, exchanges gases between the body and the environment. As air flows through the respiratory system, it passes through the nose and mouth, pharynx (FER ingks), trachea (TRAY kee uh),bronchi (BRAHN ki; singular, bronchus), and lungs. The parts of the respiratory system work together and supply the body with oxygen. They also rid the body of wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
Figure 6 Air enters the respiratory system through the nose and the mouth.Oxygen enters the blood in the lungs.
Pharynx and Trachea
Oxygen enters the body when you inhale, or breathe in. Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale. When you inhale, air enters the nostrils and passes through the pharynx. Because the pharynx is part of the throat, it is a part of both the digestive and respiratory systems. Food goes through the pharynx to the esophagus. Air travels through the pharynx to the trachea. The trachea is also called the windpipe because it is a long, tube like organ that connects the pharynx to the bronchi.
Oxygen enters the body when you inhale, or breathe in. Carbon dioxide leaves the body when you exhale. When you inhale, air enters the nostrils and passes through the pharynx. Because the pharynx is part of the throat, it is a part of both the digestive and respiratory systems. Food goes through the pharynx to the esophagus. Air travels through the pharynx to the trachea. The trachea is also called the windpipe because it is a long, tube like organ that connects the pharynx to the bronchi.
1.  Reading Check Which organ is part of both the digestive system and the respiratory system?
Reading Check Which organ is part of both the digestive system and the respiratory system?
 Reading Check Which organ is part of both the digestive system and the respiratory system?
Reading Check Which organ is part of both the digestive system and the respiratory system?
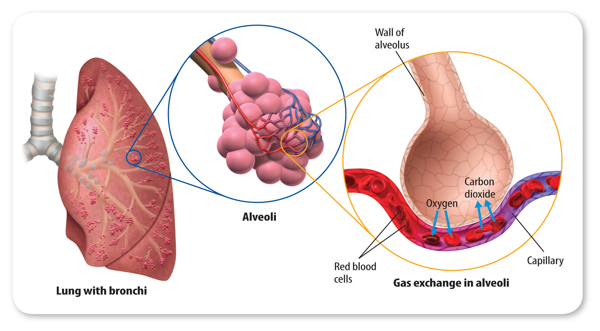
Bronchi and Alveoli
There are two bronchi; one enters the left lung, and one enters the right lung.As shown in Figure 7, the bronchi divide into smaller tubes that end in tiny groups of cells that look like bunches of grapes. These groups of cells are called alveoli (al VEE uh li). Inside each lung, there are more than 100 million alveoli. The alveoli are surrounded by blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen in the alveoli enters the capillaries. The blood inside capillaries transports oxygen to the rest of the body
There are two bronchi; one enters the left lung, and one enters the right lung.As shown in Figure 7, the bronchi divide into smaller tubes that end in tiny groups of cells that look like bunches of grapes. These groups of cells are called alveoli (al VEE uh li). Inside each lung, there are more than 100 million alveoli. The alveoli are surrounded by blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen in the alveoli enters the capillaries. The blood inside capillaries transports oxygen to the rest of the body
2. 
Reading Check What are alveoli, and what do they do?

Reading Check What are alveoli, and what do they do?
Diaphragm
Inhaling and exhaling require the movement of a thin muscle under the lungs called the diaphragm (DI uh fram). As the diaphragm contracts and moves down, air enters the lungs and you inhale. When the diaphragm relaxes and moves up, you exhale.
Figure 7 Bronchi divide into smaller tubes that end in clusters of alveoli that are surrounded by capillaries.
 Visual Check Which gas leaves the alveoli and enters capillaries?
Visual Check Which gas leaves the alveoli and enters capillaries?Lesson Assessment
Use Vocabulary
1. Use the term organ system in a sentence.
2. Define homeostasis in your own words.
3. A(n) __________ is a type of white blood cell.
Understand Key Concepts
4. Organs are groups of __________ that work together.
A.cells
B.organisms
C.systems
D.tissues
5. Which body system removes carbon dioxide and waste?
A.circulatory
B.digestive
C.excretory
D.lymphatic
6. Which body system makes immune cells?
A.circulatory
B.digestive
C.excretory
D.lymphatic
7. Which are bundles of cells in the lungs that take in oxygen?
A.alveoli
B.bronchi
C.nostrils
D.trachea
8. Which is NOT a type of blood vessel?
A.artery
B.capillary
C.spleen
D.vein
Critical Thinking
9. Summarize Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to show how nutrients travels through the
respiratory and circulatory system.
respiratory and circulatory system.
10. Compare the functions of lymphatic vessels and blood vessels.
11. Relate the organs of the lymphatic system to immunity.
12. Identify the main functions of the skeletal, muscular, respiratory,circulatory, and
integumentary systems.
integumentary systems.
Writing in Science
13. Write a five sentence paragraph that distinguishes the two main types of diseases. Be sure to include a topic sentence and a concluding sentence in your paragraph.
No comments:
Post a Comment