Homeostasis and the Human Body
Click here for today's work Link
Use your Human Body Booklet and the website to
complete page 2 & 3 in your booklet
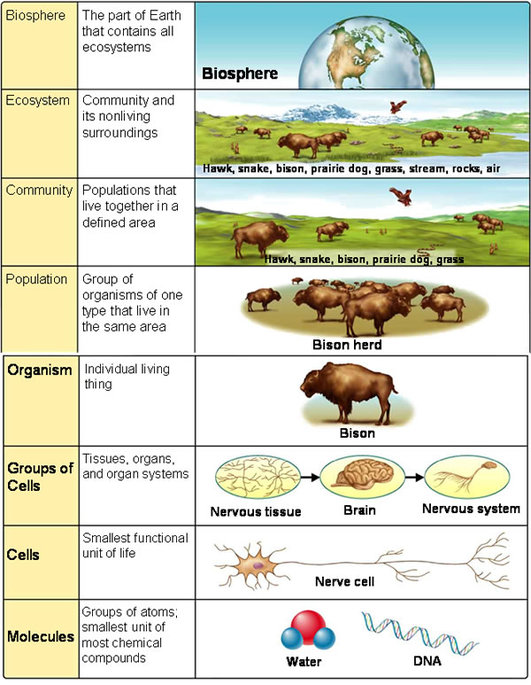
Organization of Living Things


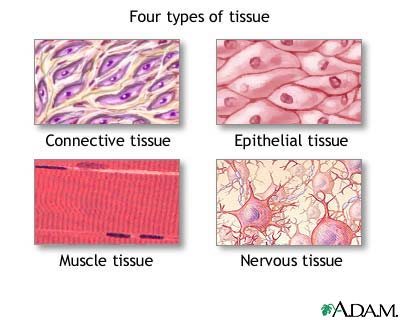
Types of Tissue
Organ Research Reference
Liver
The normal liver contains typical connective tissue.
Eyes contain 2 types of tissue

The Heart
The heart has muscle tissue and connective tissue

The Brain
What kind of tissue is the brain made out of?

Next week...
Human Body Systems
The Incredible Human Machine Video
Structure and Movement
Links
Class PowerPoint Muscles Lab The Muscular System Video The Bone Song Musculoskeletal System Video Kidport - Muscles
Learn More about Muscles Here
Muscles, Muscles, More Muscles Human Body Systems Study Incredible Human Machine Worksheet
The Muscular System works with the Skeletal System
to form the
Musculo-skeletal System.
Click here for today's work Link
Use your Human Body Booklet and the website to
complete page 2 & 3 in your booklet
Organization of Living Things


Types of Tissue

Organ Research Reference
Liver
The normal liver contains typical connective tissue.

Eyes contain 2 types of tissue

The Heart
The heart has muscle tissue and connective tissue

The Brain
What kind of tissue is the brain made out of?

Next week...
Human Body Systems
The Incredible Human Machine Video
Learn More about Muscles Here
Muscles, Muscles, More Muscles Human Body Systems Study Incredible Human Machine Worksheet
The Muscular System works with the Skeletal System
to form the
Musculo-skeletal System.
The muscular system moves the body.
The body has over 600 muscles.
The body has over 600 muscles.
Muscle: an organ that relaxes and contracts to allow movement.
In this lesson, you will read more about two organ systems—the skeletal system and the muscular system—that give the body structure, help the body move, and protect other organ systems.

1. movement 1. to produce movement
2. protection 2. to maintain posture
3. structure 3. generate heat
4. storage of minerals
5. blood cell production
The Skeletal System
The skeletal system has four major jobs.
It protects internal organs, provides support, helps the body move, and stores minerals. The skeletal system is mostly bones. Adults have 206 bones. Ligaments, tendons, and cartilage are also parts of the skeletal system.
It protects internal organs, provides support, helps the body move, and stores minerals. The skeletal system is mostly bones. Adults have 206 bones. Ligaments, tendons, and cartilage are also parts of the skeletal system.
Storage The skeletal system is also an important storage site for minerals such as calcium. Calcium is essential for life. It has many functions in the body. Muscles require calcium for contractions. The nervous system requires calcium for communication. Most of the calcium in the body is stored in bone. Calcium helps build stronger compact bone.Cheese and milk are good sources of calcium.
1.  Reading Check What mineral is stored by the skeletal system?
Reading Check What mineral is stored by the skeletal system?
 Reading Check What mineral is stored by the skeletal system?
Reading Check What mineral is stored by the skeletal system?
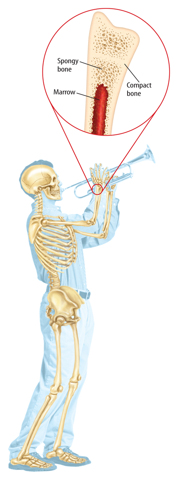
Support Without a skeleton, your body would look like a beanbag. Your skeleton gives your body structure and support, Your bones help you stand, sit up,and raise your arms to play an instrument, such as a trumpet.
Protection Many of the bones in the body protect organs that are made of softer tissue.For example, the skull protects the soft tissue of the brain, and the rib cage protects the soft tissue of the lungs and heart.
Movement The skeletal system helps the body move by working with the muscular system. Bones can move because they are attached to muscles. You will read more about
the interaction of the skeletal system and the muscular system later in this lesson.
the interaction of the skeletal system and the muscular system later in this lesson.
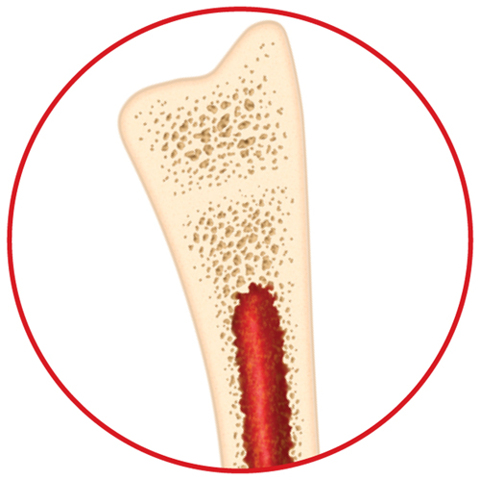
Bone Types
Bones are organs that contain two types of tissue.
Compact bone is the hard outer layer of bone.
Compact bone is the hard outer layer of bone.
Spongy bone is the interior region of bone that contains many tiny holes. Spongy bone is inside compact bone.
Some bones also contain bone marrow.
Some bones also contain bone marrow.
Bone marrow is a part of the lymphatic system and makes white blood cells.
2.  Reading Check How do the two types of bone tissue differ?
Reading Check How do the two types of bone tissue differ?
 Reading Check How do the two types of bone tissue differ?
Reading Check How do the two types of bone tissue differ?
Figure 1 Bone is made up of a dense, hard exterior and a spongy interior.
Bones Connect in several ways!

The Muscular System
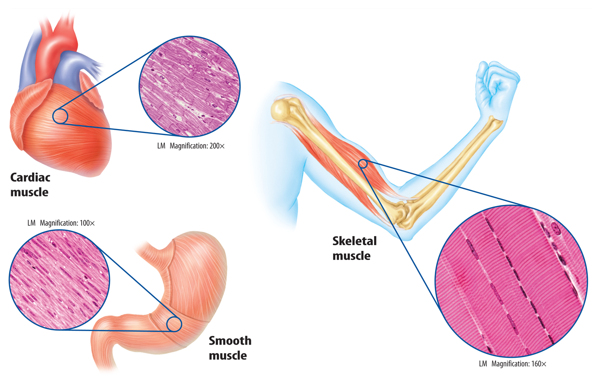
Types of muscles.
Skeletal muscles are involved in bodily locomotion.
Smooth muscles are involved in digestion
Cardiac muscles are involved within the heart.
Smooth muscles are involved in digestion
Cardiac muscles are involved within the heart.
Over all, the muscles are always involved in moving something.
Muscle Movements
Involuntary - Automatically move without you knowing.
Voluntary- Brain sends message to muscle. You control the movements
Voluntary- Brain sends message to muscle. You control the movements
Three types of muscle tissue
Skeletal muscles involve moving the body. They are voluntary muscles.
Cardiac muscles involve moving blood. They are involuntary muscles.
Smooth muscles are involved with moving material in the bowels. They are involuntary muscles.
Cardiac muscles involve moving blood. They are involuntary muscles.
Smooth muscles are involved with moving material in the bowels. They are involuntary muscles.
These muscles have distinctive attributes.
Skeletal muscles are attached to bone with tendons. They are striated, they appear in layers. Skeletal muscle works with the skeletal system and helps you move. Tendons connect skeletal muscles to bones. Skeletal muscle also gives you the strength to lift heavy objects. Skeletal muscles are also called voluntary muscles,which are muscles that you can consciously control.
Smooth muscles act together with other smooth muscles to coordinate the movement of stuff through the bowels. Smooth muscles are not striated, they are thin and line various organs. Smooth muscle tissue moves materials through your body. Smooth muscle tissue is in organs such as the stomach and the bladder. Blood vessels also have smooth muscle tissue.
Smooth muscles act together with other smooth muscles to coordinate the movement of stuff through the bowels. Smooth muscles are not striated, they are thin and line various organs. Smooth muscle tissue moves materials through your body. Smooth muscle tissue is in organs such as the stomach and the bladder. Blood vessels also have smooth muscle tissue.
Cardiac muscles are in the heart, The heart is an organ that is made of smooth muscle tissue specifically cardiac muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle is only in the heart. It continually
contracts and relaxes and moves blood throughout your body.
Muscle tissue is a specialized tissue that can contract.
 TENDONS AND LIGAMENTS (CONNECTIVE TISSUE)
TENDONS AND LIGAMENTS (CONNECTIVE TISSUE)
As fascinating as they are, muscles alone can't do the job. At every joint, tendons and ligaments also help out. Muscles wouldn't be very useful alone because they don't directly connect to the bone, so even if they contract, they wouldn't be moving anything. Instead, muscles are connected to tendons, when themselves are connected to the bones. When the muscles contract, they pull on the tendons, which in turn pull on the muscles, and that causes movement.
But without ligaments, that movement wouldn't be too useful because it would not be directed movement. Without ligaments, instead of bones bending or rotating about each other when muscles contract, they would slide by each other. Ligaments are what hold the bones together.
When tendons and ligaments are pulled beyond their normal range, a sprain occurs.
Tendons connect muscle to bone.
Ligaments connect bone to bone.
Cartilage acts as a shock absorber between bones.
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the bodies of humans and other animals, including the joints between bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs. It is not as hard and rigid as bone but is stiffer and less flexible than muscle.
But without ligaments, that movement wouldn't be too useful because it would not be directed movement. Without ligaments, instead of bones bending or rotating about each other when muscles contract, they would slide by each other. Ligaments are what hold the bones together.
When tendons and ligaments are pulled beyond their normal range, a sprain occurs.
Tendons connect muscle to bone.
Ligaments connect bone to bone.
Cartilage acts as a shock absorber between bones.
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the bodies of humans and other animals, including the joints between bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs. It is not as hard and rigid as bone but is stiffer and less flexible than muscle.
Energy changes when your muscles contract...
Eating food supplies your cells with the necessary nutrients to perform and create ATP or energy.
This is a chemical reaction, turning food into energy...(remember cellular respiration?)
 The muscles then use the energy or ATP to move, this is mechanical energy
The muscles then use the energy or ATP to move, this is mechanical energy
Eating food supplies your cells with the necessary nutrients to perform and create ATP or energy.
This is a chemical reaction, turning food into energy...(remember cellular respiration?)
Also the muscles create HEAT when they move ....This is thermal energy
The muscular system contributes to approximately 40%
of the body’s overall weight (an average sized individual.)
of the body’s overall weight (an average sized individual.)
Myology is the study of muscles
How do the muscles help your body maintain its temperature?
Muscles play a significant role in the body’s ability to maintain a constant temperature regardless of the temperature which surrounds it. Metabolism, which is the process of turning food into energy, releases heat, which in turn helps to maintain a regulated body temperature.
Muscles play a significant role in the body’s ability to maintain a constant temperature regardless of the temperature which surrounds it. Metabolism, which is the process of turning food into energy, releases heat, which in turn helps to maintain a regulated body temperature.
Muscles, which comprise approximately 40% of the body’s weight, carry enough impact on the human body based solely on their mass to be the prime source of the body’s ability to heat itself and maintain a steady constant temperature. The state of chronic muscle fiber activity maintains body temperature and the state of strenuous muscular activity increases body temperature, encouraging the human body to produce sweat to cool the temperature.
The human body can move in many different directions and perform a wide variety of tasks. It is able to do things that require many parts of the body to move, such as shooting a basketball into a hoop or swimming a lap in a pool. The human body also can remain very still, such as when posing for a picture or balancing on one leg.
You might already know that there are muscle cells in your arms and legs. But did youknow that there are muscle cells in your eyes, heart, and blood vessels?Without muscle cells you would not be able to talk, write, or run.
Muscle cells are everywhere in the body. Almost1/2 of your body mass is muscle cells. These muscle cells make up the muscularsystem. By working together, they help the body move.
3. Key Concept Check What systems help the body move?
Figure 2 Cardiac muscle is only in the heart. Organs, such as the stomach, have smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle moves your body.
 Visual Check Which type of muscle is in your arms?
Visual Check Which type of muscle is in your arms?Lesson Summary
1. . Which is NOT a type of muscle tissue?
A.cardiac
B.lymphatic
C.skeletal
D.smooth
2. Which is a part of the skeletal system?
A.ligament
B.spleen
C.thymus
D.trachea
3. Summarize Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to
show the three types of
muscle tissue.
muscle tissue.

4. Predict
the effect of having less compact bone than normal on the strength of the
skeletal system by examining the figure below. Distinguish between compact bone
and spongy bone.
skeletal system by examining the figure below. Distinguish between compact bone
and spongy bone.
Thank you and Have a good day!